OmniParser for Pure Vision Based GUI Agent
https://github.com/microsoft/OmniParser
Abstract 抽象
The recent success of large vision language models shows great potential in driving the agent system operating on user interfaces. However, we argue that the power multimodal models like GPT-4V as a general agent on multiple operating systems across different applications is largely underestimated due to the lack of a robust screen parsing technique capable of: 1. reliably identifying interactable icons within the user interface, and 2. understanding the semantics of various elements in a screenshot and accurately associate the intended action with the corresponding region on the screen. To fill these gaps, we introduce OMNIPARSER, a comprehensive method for parsing user interface screenshots into structured elements, which significantly enhances the ability of GPT-4V to generate actions that can be accurately grounded in the corresponding regions of the interface. We first curated an interactable icon detection dataset using popular webpages and an icon description dataset. These datasets were utilized to fine-tune specialized models: a detection model to parse interactable regions on the screen and a caption model to extract the functional semantics of the detected elements. OMNIPARSER significantly improves GPT-4V's performance on ScreenSpot benchmark. And on Mind2Web and AITW benchmark, OMNIPARSER with screenshot only input outperforms the GPT-4V baselines requiring additional information outside of screenshot
大型视觉语言模型的近期成功显示出驱动用户界面智能体系统运行的巨大潜力。然而,我们认为,像 GPT-4V 这样的多模态模型作为跨多个作系统、不同应用的通用代理,其强大能力被严重低估,原因是缺乏能够可靠识别用户界面中可交互图标的强大屏解析技术:1. 可靠识别用户界面中可交互的图标,2. 理解截图中各元素的语义,并准确将预期动作与屏幕对应区域关联。为填补这些空白,我们引入了 OMNIPARSER,一种将用户界面截图解析为结构化元素的综合方法,显著提升了 GPT-4V 生成能够准确扎根于界面相应区域的动作的能力。我们首先策划了一个可交互的图标检测数据集,使用了热门网页和图标描述数据集。这些数据集被用来微调专用模型:检测模型用于解析屏幕上可交互区域,字幕模型用于提取检测元素的功能语义。OMNIPARSER 显著提升了 GPT-4V 在 ScreenSpot 基准测试中的表现。在 Mind2Web 和 AITW 基准测试中,仅输入截图的 OMNIPARSER 表现优于需要额外截图信息的 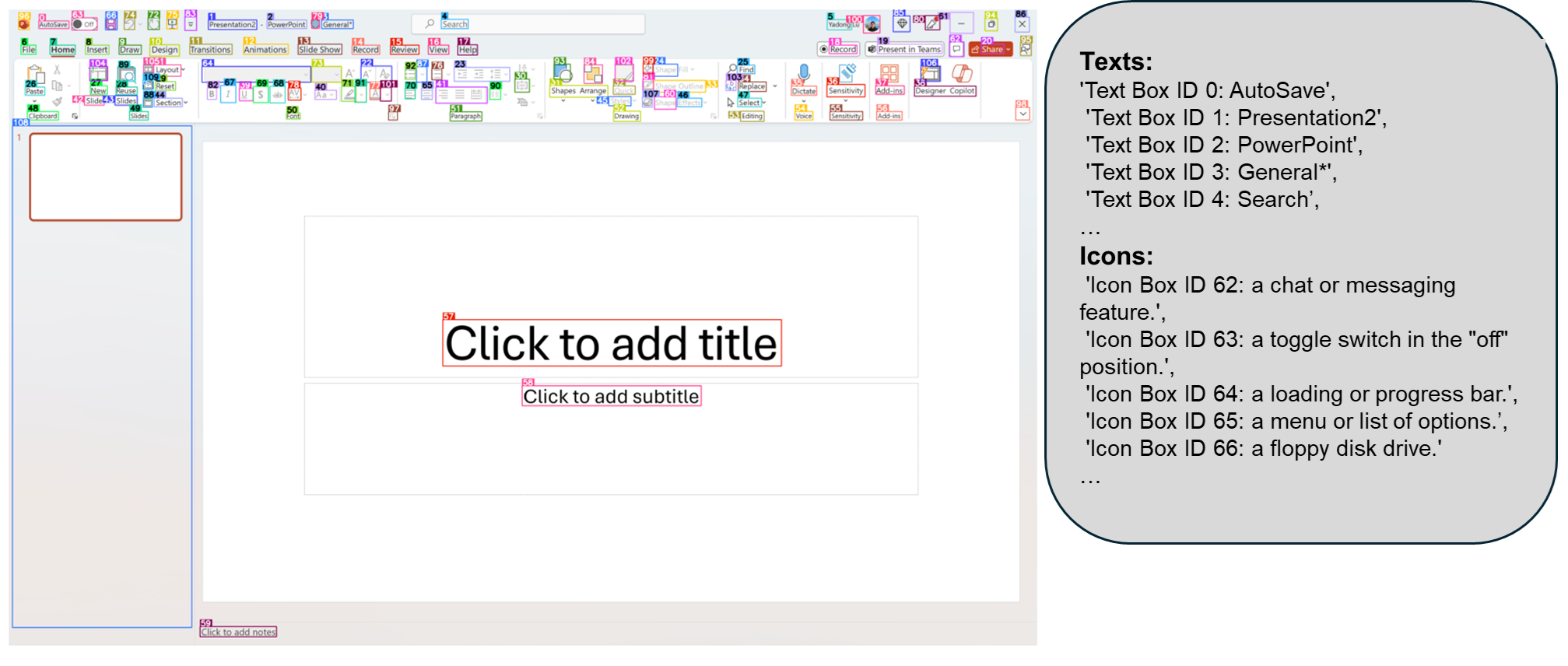 r
r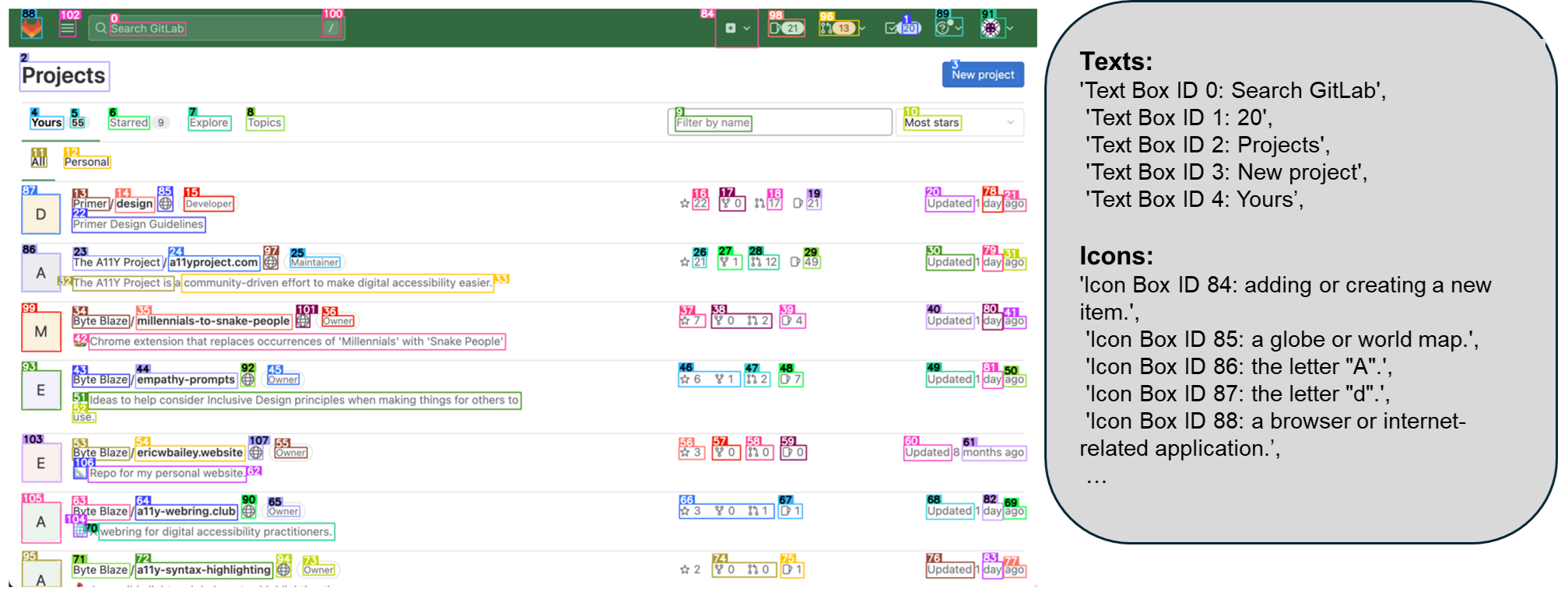 用于可交互区域检测和图标功能描述的策划数据集
用于可交互区域检测和图标功能描述的策划数据集
We curate a dataset of interactable icon detection dataset, containing 67k unique screenshot images, each labeled with bounding boxes of interactable icons derived from DOM tree. We first took a 100k uniform sample of popular publicly availabe urls on the clueweb dataset, and collect bounding boxes of interactable regions of the webpage from the DOM tree of each urls. We also collected 7k icon-description pairs for finetuning the caption model.
我们策划了一个可交互图标检测数据集,包含 67k 张独特的截图图像,每张图片都标注了可交互图标的边界框,这些图标源自 DOM 树。我们首先抽取了 clueweb 数据集中 10 万个常见公开 URL 的统一样本,并从每个 URL 的 DOM 树中收集网页可交互区域的边界方框。我们还收集了 7000 对图标-描述对,用于对说明模型进行微调。
Examples from the Interactable Region Detection dataset. . TThe bounding boxes are based on the interactable region extracted from the DOM tree of the webpage.
来自可交互区域检测数据集的示例。 这些边界框基于从网页 DOM 树中提取的可交互区域。
Results 结果
We evaluate our model on SeeClick, Mind2Web, and AITW benchmarks. We show that our model outperforms the GPT-4V baseline on all benchmarks. We also show that our model with screenshot only input outperforms the GPT-4V baselines requiring additional information outside of screenshot.
我们基于 SeeClick、Mind2Web 和 AITW 基准测试来评估我们的模型。我们证明我们的模型在所有基准测试中均优于 GPT-4V 基线。我们还展示了仅输入截图的模型表现优于需要额外信息的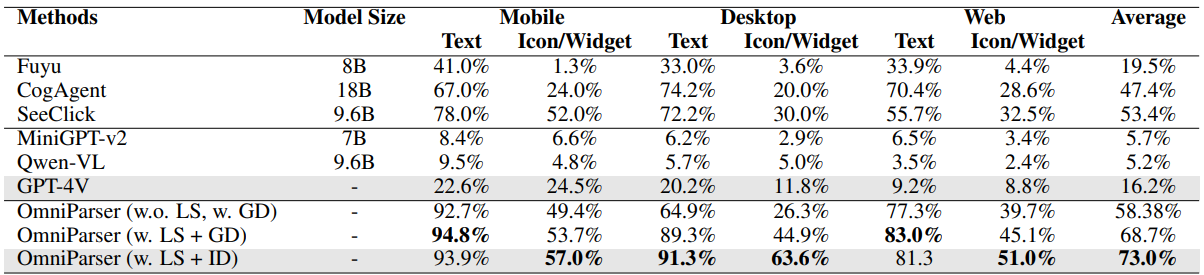 rser is a plugin choice for off-the-shelf vision langauge models, we show the performance of OmniParser combined with recently announced vision language models: Phi-3.5-V and Llama-3.2-V. As seen in table, our finetuned interactable region detection (ID) model significantly improves the task performance compared to grounding dino model (w.o. ID) with local semantics across all subcategories for GPT-4V, Phi-3.5-V and Llama-3.2-V. In addition, the local semantics of icon functionality helps significantly with
rser is a plugin choice for off-the-shelf vision langauge models, we show the performance of OmniParser combined with recently announced vision language models: Phi-3.5-V and Llama-3.2-V. As seen in table, our finetuned interactable region detection (ID) model significantly improves the task performance compared to grounding dino model (w.o. ID) with local semantics across all subcategories for GPT-4V, Phi-3.5-V and Llama-3.2-V. In addition, the local semantics of icon functionality helps significantly with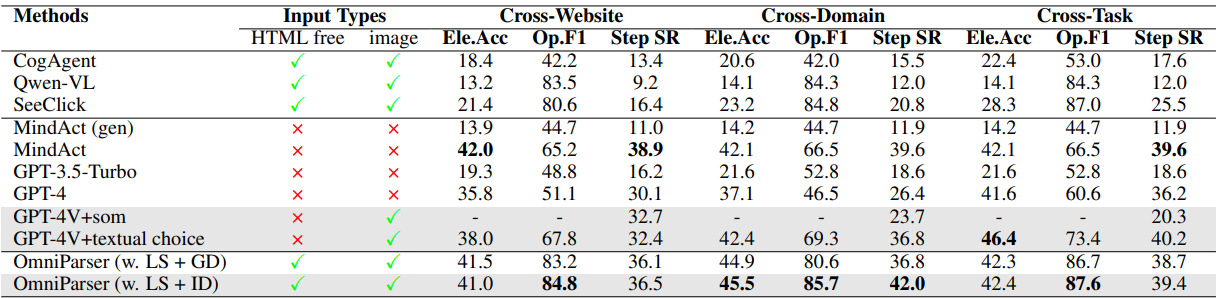 g
g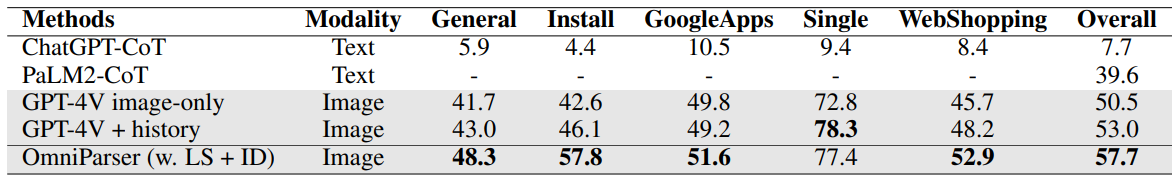
评论